Evolutionary Algorithm
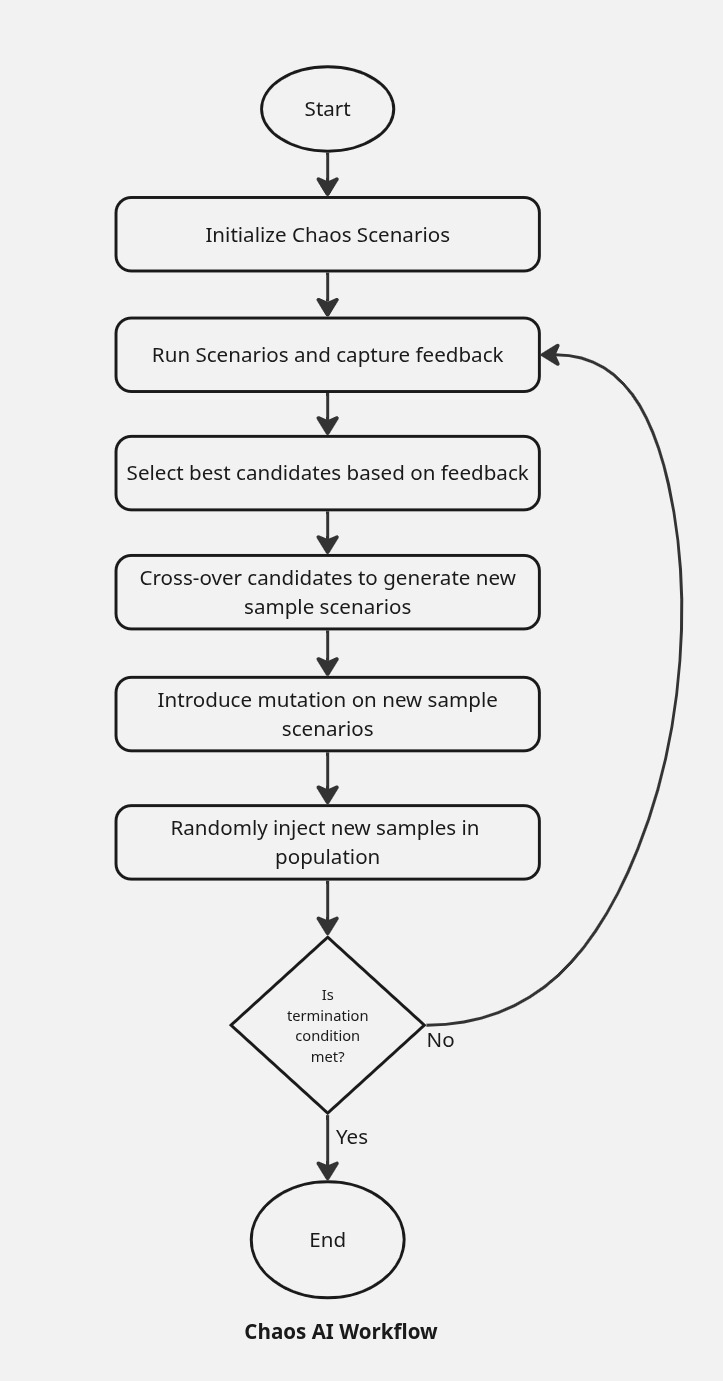
Krkn-AI uses an online learning approach by leveraging an evolutionary algorithm, where an agent runs tests on the actual cluster and gathers feedback by measuring various KPIs for your cluster and application. The algorithm begins by creating random population samples that contain Chaos scenarios. These scenarios are executed on the cluster, feedback is collected, and then the best samples (parents) are selected to undergo crossover and mutation operations to generate the next set of samples (offspring). The algorithm relies on heuristics to guide the exploration and exploitation of scenarios.
Terminologies
- Generation: A single iteration or cycle of the algorithm during which the population evolves. Each generation produces a new set of candidate solutions.
- Population: The complete set of candidate solutions (individuals) at a given generation.
- Sample (or Individual): A single candidate solution within the population, often represented as a chromosome or genome. In our case, this is equivalent to a Chaos experiment.
- Selection: The process of choosing individuals from the population (based on fitness) to serve as parents for producing the next generation.
- Crossover: The operation of combining two Chaos experiments to produce a new scenario, encouraging the exploration of new solutions.
- Mutation: A random alteration of parts of a Chaos experiment.
- Scenario Mutation: The scenario itself is changed to a different one, introducing greater diversity in scenario execution while retaining the existing run properties.
- Composition: The process of combining existing Chaos experiments into a grouped scenario to represent a single new scenario.
- Population Injection: The introduction of new individuals into the population to escape stagnation.
Configurations
The algorithm relies on specific configurations to guide its execution. These settings can be adjusted in the Krkn-AI config file, which you generate using the discover command.
generations
Total number of generation loop to run (Default: 20)
- The value for this field should be at least 1.
- Setting this to a higher value increases Krkn-AI testing coverage.
- Each scenario tested in the current generation retains some properties from the previous generation.
population_size
Minimum Population size in each generation (Default: 10)
- The value for this field should be at least 2.
- Setting this to a higher value will increase the number of scenarios tested per generation, which is helpful for running diverse test samples.
- A higher value is also preferred when you have a large set of objects in cluster components and multiple scenarios enabled.
- If you have a limited set of components to be evaluated, you can set a smaller population size and fewer generations.
crossover_rate
How often crossover should occur for each scenario parameter (Default: 0.6 and Range: [0.0, 1.0])
- A higher crossover rate increases the likelihood that a crossover operation will create two new candidate solutions from two existing candidates.
- Setting the crossover rate to
1.0ensures that crossover always occurs during selection process.
mutation_rate
How often mutation should occur for each scenario parameter (Default: 0.7 and Range: [0.0, 1.0])
- This helps to control the diversification among the candidates. A higher value increases the likelihood that a mutation operation will be applied.
- Setting this to
1.0ensures persistent mutation during the selection process.
scenario_mutation_rate
How often a mutation should result in a change to the scenario (Default: 0.6; Range: [0.0, 1.0])
- A higher rate increases diversity between scenarios in each generation.
- A lower rate gives priority to retaining the existing scenario across generations.
composition_rate
How often a crossover would lead to composition (Default: 0.0 and Range: [0.0, 1.0])
- By default, this value is disabled, but you can set it to a higher rate to increase the likelihood of composition.
population_injection_rate
How often a random samples gets newly added to population (Default: 0.0 and Range: [0.0, 1.0])
- A higher injection rate increases the likelihood of introducing new candidates into the existing generation.
population_injection_size
What’s the size of random samples that gets added to new population (Default: 2)
- A higher injection size means that more diversified samples get added during the evolutionary algorithm loop.
- This is beneficial if you want to start with a smaller population test set and then increase the population size as you progress through the test.
wait_duration
Time to wait after scenario execution. Sets Krkn’s --wait-duration parameter. (Default: 120 seconds)
stopping_criteria
Configuration for advanced stopping conditions based on fitness, saturation, or exploration limits. See Stopping Criteria for full details.